MPUSEP (MADHYA PRADESH URBAN SENITATION AND ENVIRONMENT PROGRAMME)
PROJECT:
Madhya Pradesh Urban Sanitation & Environment Programme (MPUSEP)
OVERVIEW:
Madhya Pradesh (MP) is geographically the second largest and eighth most urbanized
state in India. At present, MP’s total urban population is of 20.1 million (28%
of total population) concentrated in 476 urban centers as follows: 378 municipal
bodies of which 16 are Municipal Corporations (Nagar PalikNigams), 98 are Municipal
Councils (Nagar PalikaParishad), and 264 are Nagar Parishads, and 98 Census Towns.
Of the 16 Municipal Corporations, four are million-plus cities, namely Indore, Bhopal,
Jabalpur, and Gwalior.
In the cities in MP, household access to piped water supply ranges between 35 to
150 lpcd(litres per capita per day);access to underground sewerage range between
zero to 40%, waste collection ranges between 85-90%, and 60-80% of rainwater run-off
is effectively drained.
Rapid urbanization has resulted in increasing pressure on existing urban infrastructure
which not only needs to be maintained, but expanded to cover the new areas of urbanization.
The key infrastructure sectors which need immediate attention are the augmentation
of Water Supply with achievement of Service levels, providing safe and clean environment
through underground sewerage and wastewater treatment, Management of Municipal Solid
waste.
The State Government proposed the MPUSEP, and successfully received financial assistance
from the KfW development bank of Germany; the project will have a positive environmental
impact in the State of Madhya Pradesh.
OBJECTIVE:
The project comprises of the construction of centralised wastewater collection systems
in 5 cities along the Narmada with 100% household coverage. All five townaffect
the water quality of the river Narmada which is the most holy river and life line
of Madhya Pradesh.The Programme received a loan for the 5 sewerage systems, as well
as a grant for Accompanying Measures (AMC) to support effective implementation of
the sewerage systems and acceptance by the people. The loan, as well as the grant
form part of the bilateral agreement between the Germany and India and is routed
through the German Bank ‘KreditanstaltfürWiederaufbau’ (KfW).
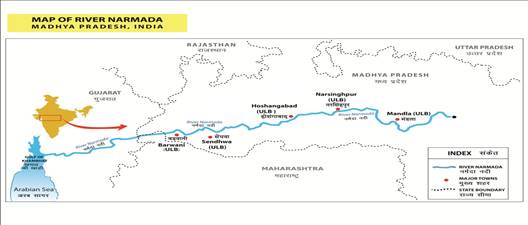
Thefollowing towns (total population of 370,000 people, with projected populations
in 2016) will receive sewerage systems and Accompanying Measures support:
- Hoshangabad (127,677)
- Narsinghpur(63,338)
- Sendhwa (60,253)
- Barwani (59,499)
- Mandla (59,248)
The Project Implementing Agency (PIA) “Madhya Pradesh Urban Development Company
/ MPUDC” implements the programme through Project Management Unit at MPUDC, Bhopal,
with its decentralised PIUs (Project Implementation Units) in Hoshangabad, Indore
and Jabalpur. The PMU is being supported by the PMC (Project Management Consultant)
and the AMC (Accompanying Measures Consultant).
The length of the sewer systems to be installed in the 5 towns is approximately
650 km, including 7 STPs and 22 SPS. Further to the construction measures the Consultant
will provide services as an AMC (Accompanying Measures Consultant) for general technical
assistance and management support to the PIA (Project Implementation Agency), the
Project Implementing Units (PIUs) and the 5 ULBs (Urban Local Bodies). The AMC concentrates
supports institutional development and general capacity building for all main stakeholders
(PIA, PMU, regional PIUs, Project Monitoring teams) and specifically assistance
to urban local bodies.
MAIN STAKEHOLDERS
There is a separate ministry for Urban Development and Housing in Government of
Madhya Pradesh headed by a cabinet minister. The Urban Development and Housing Ministry
is supported by Urban Development and Housing Department (UDHD) headed by a Principal
Secretary. The key-task of the department is to provide technical, financial, administrative,
policy and legal support to various 379 municipal governments and make them efficient
for urban service delivery. Whereas the responsibility of constructing, developing,
operating and managing urban infrastructure and basic services have been devolved
to the ULBs. The fast pace of urbanization has, at the same time, imposed increasing
pressures on urban governance.
In view of the capacity constraints of the ULBs, the Government of Madhya Pradesh
(GoMP) has formed the MPUDC to support the ULBs in their respective tasks.
The Madhya Pradesh Urban Sanitation and Environment Programme (MPUSEP)is implemented
in cooperation with the Urban Development and Housing Department (UDHD) as Project
Executing Agency (PEA), through its nascent Madhya Pradesh Urban Development Company
(MPUDC) as the Project Implementing Agency (PIA). The Programme cities (ULBs) are
the final beneficiaries. MPUDC manages preparation and implementation of all urban
infrastructure programmes, including those co-financed by international financing
institutions (IFI).
It is the MPUDC and the five ULBs which are supported by an international consultant..
Within its structure, MPUDC established a Project Management Unit (PMU). The international
Consultants responsible for project management and accompanying measures are directly
linked to the PMU. The PMU is working through PIU units at lower levels in the different
divisions each one being responsible for the projects within its political limits
(PIU in Bhopal/ Hoshangabad (Hoshangabad), Indore (Barwani, Sendhwa), Jabalpur (Narsinghpur,
Mandla)). The PIUs are supported by the Project Management Consultant as well.
Management Organigram
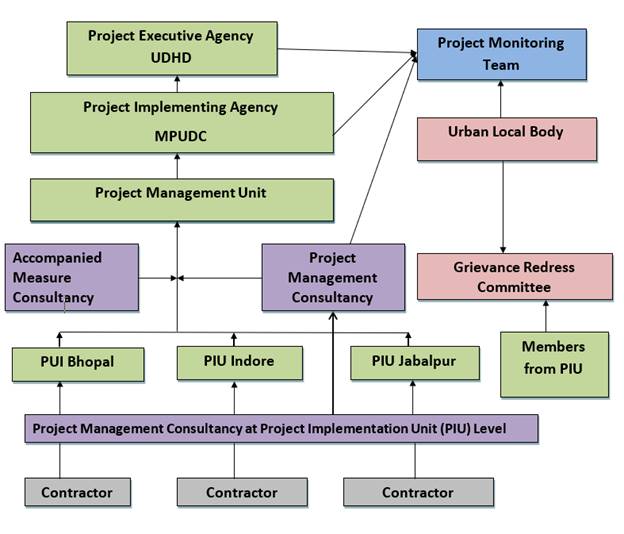
Implementation Concept – roles and responsibilities:
The GoMP / Department for Urban Development and Housing (UDHD):
- Isthe Project Executing Agency (PEA) andresponsible for overall strategic planning,
guidance and management of the Programme.
MPUDC:
- Isthe Project Implementation Agency (PIA)
- Responsible for planning, implementing, monitoring and overall supervising, and
coordinating all Programme activities.
- Prepare annual work programs, budgets and procurement plans, disburse funds and
hold regular review meetings, as well as contract and supervise project staff, prepare
reports and other documents, and provide quality control.
- Contract management on behalf of ULBs (of contractor)
PMU:
- Implementation of the Programme supported by the regional PIUs in Bhopal, Indore
and Jabalpur responsible for the actual implementation and supervision of the sub-projects
in the 5 towns
PMC/AMC:
- Technical assistance supporting during project implementation and for institutional
strengthening of the MPUDC and ULBs.
Contractor:
- Building and Operation &Maintenance for 10 years
ULBs:
- Owner of the assets and responsible for Operation & Maintenance after 10 years
- Cooperate closely during the preparation and implementation of the subprojects and
the responsibilities (rights determined in a tripartite agreement between MPUDC,
UDHD and the ULB, defining respective roles and responsibilities with financial
obligations)
PMT (Project Monitoring Team): ensure implementation/application
of TPIA
- Coordinate physical implementation with the ULB
- Ensure awareness building measures take place within the ULB
- ULB stepwise prepares itself to be able to cover operation and maintenance costs
out ofrevenues of water supply and sewage
- (ULB and PMT to be supported by AMC)
LOCATION MAP OF MPUSEP
Project Consultancy Services
The PMC (Project Management Consultant) covers the services concerning the assistance
during tendering and the award of contract, design review, construction supervision,
contract management and assistance during DNP for the sewer system, STPs (Seweage
Treatment Plants) and SPSs (Sewage Pumping Stations), tendered as DBO (Design-Build-Operate)
projects in the five towns Barwani, Hoshangabad, Mandla, Narsinghpur and Sendhwa.
The AMC (Accompanying Measures Consultant) covers the services for:::
- Institutional strengthening and capacity development for MPUDC
- General management and technical assistance for PMU, PIU, PMT and ULBs
- Development and introduction of cost-covering tariff systems in accordance to the
State tariff policy for water and sewerage
- GIS mapping of existing infrastructure in the ULBs
- Improvement of collection efficiency
- Information and awareness campaigns for the benefitting population on various topics
.
The duration of the consultancy is estimated to be approximately 48 months:
- Tendering: 6 months
- Design phase: 6 months
- Construction:
- 24 months for Barwani, Mandla, Narsinghpur and Sendhwa
- 24 months for Hoshangabad
- • DNP:12 months
The PMC/AMC is covered by the consulting consortium ofGITEC-IGIP GmbH, GITEC India,
DASTUR and UNITY. GITEC-IGIP GmbH is agerman company that offers cross-disciplinary
consulting services for development projects all over the world..GITEC has been
involved in the success of hundreds of development projects since the company’s
creation in 1977.GITEC-IGIP GmbH is a member of GITEC-IGIP Holding,
which comprises a permanent network of 15 companies in Africa, Asia, Europe
and South America. GITEC work with people and international and local partners who
have a sustained record of providing successful project support and long-term business
relationships are key to the success of GITEC. GITEC works in the field of water
and sanitation, transport and construction, natural resource and rural development,
environment and climate change, helath, development assistance, waste and energy.
INFORMATION MATERIAL / DOWNLOADS
- Leaflet Barwani English
- Leaflet Barwani Hindi
- Leaflet Sendhwa English
- Leaflet Sendhwa Hindi
- Leaflet Hoshangabad English
- Leaflet Hoshangaba Hindi
- Banner MPUSEP
- Poster MPUSEP
Barwani
About Barwani:
Barwani is a district town situated in the South Western part of Madhya Pradesh.
The district Barwani was formed on25th May 1998and is the administrative headquarters
of Barwani District. Town Barwani was the capital of old Barwani State before 1948.
This small State was spared by British, Mughals and Marathas because of its rocky
terrain and less productive soil. The Rana dynasty ruled the state throughout the
history.
The name Barwani originated from the forests of “Bad” which had surrounded the city
in old times. “Wani” is the old word for the ‘gardem’. Barwani is still pronounced
as Badwani but it spells Barwani. Barwani is situated on the south-west side of
Madhya Pradesh, andthe holy River Narmada is its northern border. The district is
surrounded by the forest ranges of Satpudato the Southand Vindhyachal to the North.
It is situated in between Latitude 22°03' north and Longitude 74°09'east, and has
an average elevation of 178 metres (583 feet). The River Narmada flows through Barwani
(just 5 km from the city). The temperature of Barwani in April and May goes as high
as 48 degrees Celsius, making it the hottest placein India. The town Barwani is
situated near the left bank of the Narmada River.
Salient features of Barwani city:
- Connected to the Agra-Mumbai NH 3
- Population: 64100
- Households: 10380
- Road Network: 149 km
- Town area: 27 sq. km
- Elevation: 178 m
Website: -www.barwani.nic.in
Map of Barwani:
Present sewerage situation in Barwani
- No integrated sewerage system existent for Barwani
- All sewerage from households and other entities flows in drains and finally into
nalas and the Holy River Narmada
- With 135 lpcd water supply there is urgent need for sewerage system (collection,
treatment and disposal)
Benefits to the whole population of Barwani
- More hygiene and better health for all.
- Free sewerage water connection to every household.
- No more open sewerage water.
- World-class sewerage water treatment and reuse of water.
- Strong urban local bodies to assure good services to the people.
- Beautification of the town.
Objectivesfor the city Barwani
- Protect the Holy River Narmada
- Provision of sanitation services (100% household connections)
- Sewerage treatment
- Strengthening of Urban Local Bodies to ensure continued sewerage services for the
population
MPUSEP – Programme measures in Barwani
- Sewer lines: 220km
- House Chambers: 3400
- Sewerage Treatment Plant: 1
- Pumping Stations: 1
- Intermediate Pumping Station:2
Note: Calculated for a population of 96300 in 2048 against present population of
64100
Details of the project work under MPUSEP in Barwani
- 1 no. Sewage Treatment Plant (STP) having capacity 9.00 MLD (based on SBR technology).
- 1 Main pumping station and 2 Intermediate Pumping Stations
- Sewer Network 220000 Meters DWC HDPE pipe 150-400 mm diameters & RCC NP3 Pipe
of diameters from 450 mm to 700mm;DI K7 PIPE 200 to 600 mm.
- Construction of 5249 Nos. of circular manholes of various sizes with vertical drop
manhole.
- Total number of House connection estimated in the year 2021 is 10500.
- Operation & Maintenance -10 years.
Hoshangabad is a city in the Western part ofMadhya Pradesh
on the south bank of the Narmada River. Hoshangabad is the administrative center
of Hoshangabad District.
The city is named after the ruler of Narmadapuram: Hoshang Shah. The city was earlier called Narmadapuram after
the Narmada
River. Later the name was changed to Hoshangabad after Hoshang Shah, the first ruler of Malwa. Hoshangabad district was part of the Nerbudda (Narmada) Division of
the Central
Provinces and Berar, which became the state of Madhya Bharat (later Madhya Pradesh) after India's independence in
1947.
The city is famous for its beautiful ghats along the banks of the Narmada river.
Sethanighat is
a major attraction. There are colourful celebrations in the city on Narmada Jayanti.
A SatsangBhavan on the ghat has regular visits by Hindu saints who hold regular
religious discourses on Ramcharitmanas and Geeta.The city has a traditional way of living
with many engaged in occupations enough for sustaining life. The city has abundant
availability of water. Hoshangabad has high income per capita amongst cities of
Madhya Pradesh.
In Hoshangabad city, there is only one industrial establishment: the Security Papers
Mill Hoshangabad, a unit of Printing and Minting Corporation of India Ltd. The main
trade in the district are handicraft, silk, leather, pulses etc. Other than these,
the main business deals in the delivering of sand and tiles which come from river
Narmada.
Salient features of Hoshangabad city:
- District town situated in the central part of Madhya Pradesh
- On the south bank Holy River Narmada
- Population: 152856
- Households: 27948
- Road Network: 310 km
- Town area: 54.08 sq. km
- Elevation: 278 m
Website: -www.mchoshangabad.com
Map of Hoshangabad:
Present situation in Hoshangabad
- No integrated sewerage system existent for Hoshangabad
- All sewerage from households and other entities flows in drains and finally into
nalas and the Holy River Narmada
- With 135 lpcd water supply there is urgent need for sewerage system (collection,
treatment and disposal)
Benefits to the whole population of Hoshangabad
- More hygiene and better health for all
- Free sewerage water connection to every household
- No more open sewerage water
- World-class sewerage water treatment and reuse of water
- Strong urban local bodies to assure good services to the people
- Beautification of the town
MPUSEP – Programme measures in Hoshangabad
- Sewer lines: 196km
- House Chambers: 13974
- Sewerage Treatment Plant: 1
- Pumping Stations: 1
- Intermediate Pumping Stations:4
Note: Calculated for a population of 245440 in 2048 against present population of
152856
Objectives
- Protect the Holy River Narmada
- Provision of sanitation services (100% household connections)
- Sewerage treatment
- Strengthening of Urban Local Bodies to ensure continued sewerage services for the
population
DETAILS OF WORK UNDER WASTE WATER AND SANITATION SECTOR
- 1Sewage Treatment Plant having capacity 21.00 MLD (based on SBR technology).
- 1 Main Pumping Station and 4 Intermediate Pumping Stations
- Sewer Network 196000 meters DWC HDPE pipe 150-400 mm diameters & RCC NP3 Pipe
of diameters from 450 mm to 900mm;DI K7 PIPE 150 to1000 mm.
- Construction of 3165 Nos. of circular manholes of various sizes with vertical drop
manhole.
- Total number of house connection estimated in the year 2021: 27948.
- Operation & Maintenance by the Contractor: 10 years.
Mandla
Mandla is a town with municipality in Mandla district in Eastern part ofMadhya Pradesh state. It is the administrative
headquarters of Mandla District. The town is picturesquely situated in a loop of
the Narmada
River, which surrounds it on three sides. For 15 miles between Mandla and Ramnagar the
river flows in a deep bed unbroken by rocks. The Narmada is worshiped here, and
many beautiful ghats have
been constructed on the banks of the river.
It was a capital of the Gondwana dynasty. The Gondwana dynasty of Garha-Mandla commenced,
according to an inscription in the palace of Namnagar in the fifth century, with the
accession of JadhoRai. The Garha-Mandla kingdom was a petty local chiefship until
the accession of RajeSangram Shah Madawi, the forty-seventh king, in 1480. This
prince extended his dominions over the Narmada Valley, and possibly Bhopal, Sagar, and Damoh and most of the Satpura hill country, and
left fifty-two forts or districts to his son. In addition to Mandla, Jabalpurand Garha in Jabalpur District and Ramnagar in
Mandla District served at times as capitals of the kingdom.
Salient features of Mandla city:
- District town situated in the east central part of Madhya Pradesh
- Holy town situated on the bank of river Narmada
- Population: 80000
- Households: 13200
- Road Network: 115 km
- Town area: 10.83 sq. km
- Elevation: 445 m
Website:
www.nagarpalikamandla.com
Map of Mandla:
Present sewerage situation in Mandla
- No integrated sewerage system existent for Mandla
- All sewerage from households and other entities flows in drains and finally into
nalas and the Holy River Narmada
Benefits to the whole population of Mandla
- More hygiene and better health for all
- Free sewerage water connection to every household
- No more open sewerage water
- World-class sewerage water treatment and reuse of water
- Strong urban local bodies to assure good services to the people
- Beautification of the town
MPUSEP – Programme measures in Mandla
- Sewer lines: 149km
- House Chambers: 4400
- Sewerage Treatment Plant: 2
- Pumping Stations: 2
- Intermediate Pumping Station:11
- Operation and Maintenance by Contractor: 10 years
Total number of House connection estimated in the year 2021:13200.
Construction of 4631 Nos. of circular manholes of various sizes with vertical drop
manhole.
Note: Calculated for a population of 120000 in 2048 against present population of
80000
Objectives
- Protect the Holy River Narmada
- Provision of sanitation services (100% household connections)
- Sewerage treatment
- Strengthening of Urban Local Bodies to ensure continued sewerage services for the
population